Impact of the Composition of Alcohol/Water Dispersion on the Proton Transport and Morphology of Cast Perfluorinated Sulfonic Acid Ionomer Thin Films
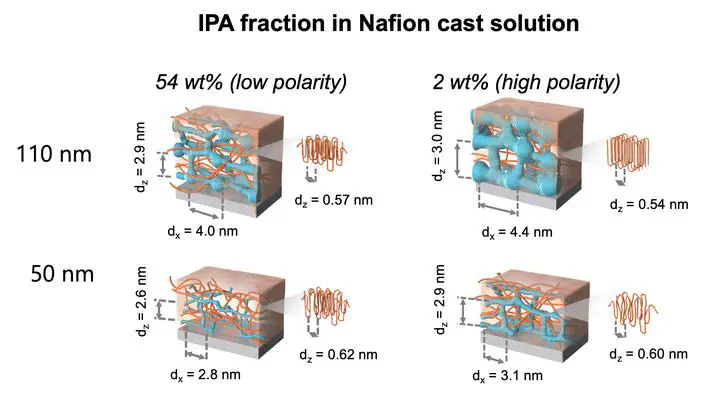 Image credit: Unsplash
Image credit: UnsplashAbstract
The dispersion of perfluorinated sulfonic acid ionomers in catalyst inks is an important factor that controls the performance of catalyst layers in membrane electrode assemblies of polymer electrolyte fuel cells. Herein, the effects of water/ alcohol compositions on the morphological properties and proton transport are examined by grazing incidence small-angle X-ray scattering, grazing incidence wide- angle X-ray scattering, and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The thin films cast by a high water/alcohol ratio Nafion dispersion have high proton conductivity and well- defined hydrophilic/hydrophobic phase separation, which indicates that the proton conductivity and morphology of the Nafion thin films are strongly influenced by the state of dispersion. This finding is expected to further understand the morphology and proton transport properties of Nafion thin films with different water/alcohol ratios, which has implications for the performance of the Pt/Nafion interface.
Add the publication’s full text or supplementary notes here. You can use rich formatting such as including code, math, and images.